Eye hand coordination, also known as visual motor integration, refers to the ability to bring movements of the eyes and hands together to complete a task. Eye hand coordination also requires attention and organization since eye movements generally lead the way for planned moves of the body, arms, and hands.

Eye hand coordination typically places emphasis upon paired moves of the eyes and the hands. However, visual motor integration can also incorporate movement patterns of the entire body. For instance, when a soccer player dribbles a ball toward the goal, the entire body becomes involved in pairing eye movements with those of the trunk, legs and feet.
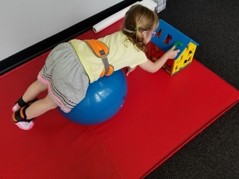
The girl shown in the photos below will use her eyes to aim for the target in a similar manner, and turn the letter correctly before she pushes her body forward. When she reaches her target, she will easily be able to place the letter into the slot on the roof of the alphabet house.
How are eye hand coordination skills used at home and at school?
Eye hand coordination skills are used at home every day during self-care activities. At home, tasks such as using utensils, clothing fasteners and personal care items all require use of eye hand coordination skills. At school, activities such as handwriting, art projects, and use of classroom manipulatives such as pencils all involve eye hand coordination.
Children who have poor eye hand coordination often have difficulty with precision in terms of eye movements. They also often have difficulty with precision when attempting to handle objects. For example, due to poor precision with eye movements and hand skills, these children are often “sloppy eaters” at the table. Food typically will spill off their plates, or drop from their utensils during mealtimes. Glasses filled with liquids such as water, milk or juice tend to get knocked over if not positioned strategically.

Children with poor eye hand coordination tend to have frequent mishaps with learning materials and toys. Their equipment is often torn, or broken due to poor use of force as the children use these materials. The difficulties often tend to have a negative impact on learning as both parent and child become frustrated.
What you can do to help
Parents and teachers can help to promote eye hand coordination skills by strengthening underlying skills that support pairing of eyes and hands working together.
- Attention can be strengthened through the use of active physical exercise. Moving the body as a whole helps muscles of the body learn to work together.
- Eye exercises, for example, eye tracking activities including ball games, puzzles, and visual perceptual worksheets can be valuable in training eye movements to work together with other visual perceptual skills.
- Construction toys that involve the use of tools are helpful in developing hand skills that support movements of the eyes that lead the hands into action.
For more information about eye hand coordination skills, refer to the following posts:







Comments are closed.